Biliary Atresia Detection
- Biliary Atresia detection using color clustering and Nearest Neighbor classification: A user interactive approach:
[GitHub]
Biliary Atresia (BA) refers to a disease that mostly affects newborns by partially obstructing
the bile ducts from the liver to the intestines, causing the trapped bile to damage the liver
itself and often resulting in the need for a transplant. To detect BA, expert personell (e.g., pediatricians)
or non-experts (e.g., the parents) usually analyze the color of the feces with the help of a
reference stool color card. To automate this process, some approaches in the literature proposed
smartphone apps enabling the parents to capture an image of the feces, select a point of the image to
analyze, and compare it with the stool color card. However, such approaches consider only the local
pixel chosen for matching and are therefore highly dependent on the position chosen by the user, who may
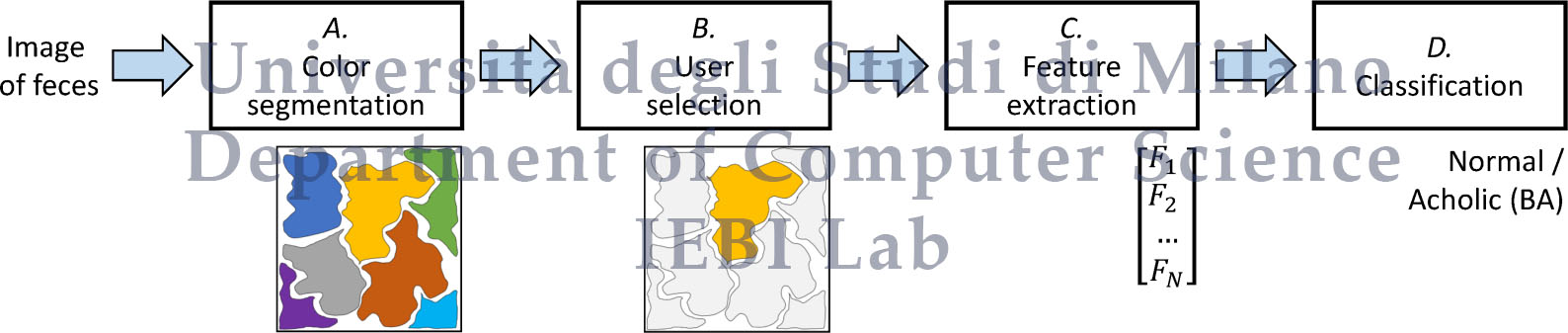
choose a non-significant pixel to perform the analysis. In this work, we propose the first method in the
literature for BA detection that considers a color-based segmentation and a nearest neighbor classification.
Differently than the approaches in the literature, the color segmentation clusters the image in different
areas based on the color and permits to automatically and robustly consider the corresponding cluster,
and not only the local pixel, to perform the classification. Results on a database captured in uncontrolled
conditions show the validity of the approach.
Project page: https://iebil.di.unimi.it/avb/index.htm